Qinghai-Tibet Railway and Tibet’s Industrial Restructuring
2006-09-11
By Guo Lihong
Research Report No 009, 2006
The completion of the Qinghai-Tibet Railway will trigger an economic radiation that is characteristic of point and axis development, which will greatly promote the adjustment of Tibet’s economic and industrial structures.
I. Comparative Analysis of Tibet’s Economic Structure
Nationally, the provinces, municipality and autonomous regions in western China are all noted for their relatively low level of social and economic development. This article makes horizontal comparison, taking Tibet as one of the 12 western provinces, municipality and autonomous regions in China.
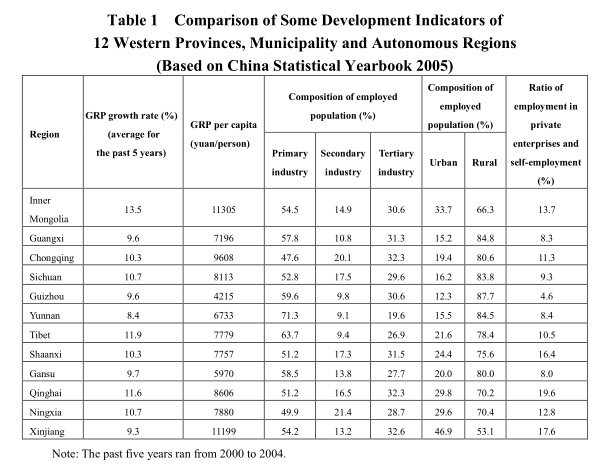
1. Urbanization plays a far greater role than in inland
The development indicators in Table 1 show that Tibet is at the middle level of development among the 12 western provinces, municipality and autonomous regions and it has demonstrated some unique features.
First, Tibet’s gross regional product (GRP) grew at an average annual rate of 11.9 percent during the five years from 2000 to 2004. The growth rate was the second highest, next only to Inner Mongolia (13.5 percent).
Second, Tibet’s per capita GRP in 2004 was 7,779 yuan and its ratio of employment in private enterprises and self-employment was 10.5 percent. Both indicators ranked seventh, at the medium level.
Third, the composition of the employed population is in sharp contrast to that in other regions. In terms of residences, the ratio of Tibet’s urban employment to its total employed population was 21.6 percent, ranking sixth and being still at the middle level. But in terms of industrial classification, Tibet’s primary industry accounted for 63.7 percent of its total employment, while its secondary and tertiary industries respectively accounted for 9.4 percent and 26.9 percent all of which are only better than Yunnan.
This contrast indicates that since Tibet is vast but sparsely populated, it can hardly expand employment in the secondary and tertiary industries in rural areas like inland places. For this reason, its ratio of employment in the secondary and tertiary industries is not dramatically different from the ratio of its urban employment to its total employed population. It also suggests that urbanization will play a far greater role in Tibet’s industrial restructuring than in inland places.
2. Urban conditions are relatively poor
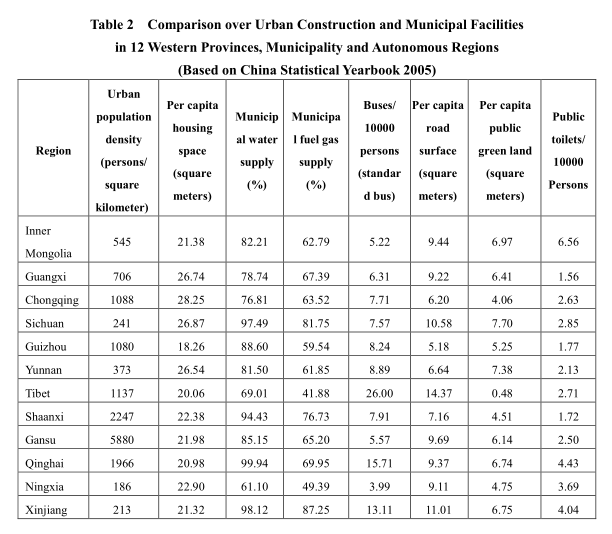
…
If you need the full text, please leave a message on the website.














