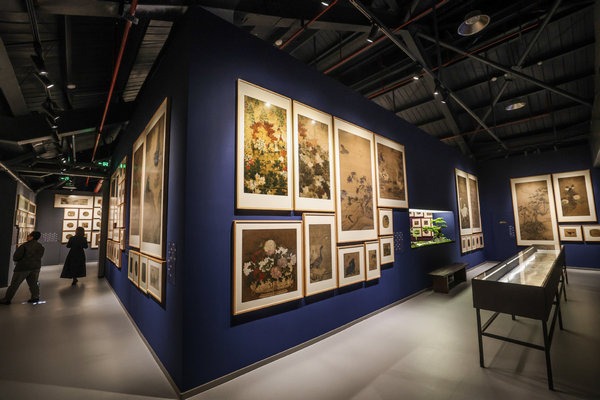
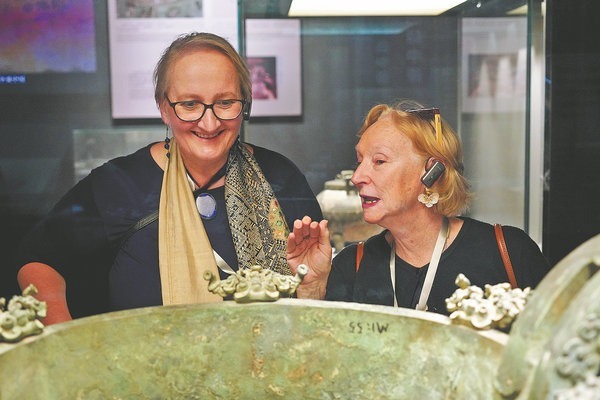
Museum showcases Shanxi's ancient heritage
Relics discovered at Taosi archaeological site highlight province's role as cradle of early Chinese civilization


Prehistoric observatory
The guibiao on display in the museum is a part of an ancient observatory discovered at the Taosi ruins. Archaeologists believe this is the earliest observatory known in China.
The most exciting part of the observatory are 13 rammed-earth columns arranged in a semicircular shape, Gao said.
"We didn't know the function of the columns at the beginning," Gao said. "However, after years of observation of the columns' projection under the sun, we realized this was the site of an ancient observatory, with the columns used to measure the sun's beam angle and determine the 24 zodiac terms of a year."
He explained that, standing at a specific observation point, observers could determine the solar terms based on the position of the sun during sunrise. For example, the winter solstice occurs when the sun rises from the second narrow gap between the columns, while the spring and autumn equinoxes are marked by the seventh gap.
The establishment of the 24 zodiac terms is believed to be an outstanding contribution to the world made by ancient Chinese almanac scientists.
The system of the zodiac terms, used by Chinese people to guide agricultural production in both ancient and modern times, was recognized as an intangible cultural heritage item by UNESCO in 2016.