Cometh the crisis, cometh the reform


ChiNext board's new IPO system to boost innovative startups, link capital market to post-COVID economic goals
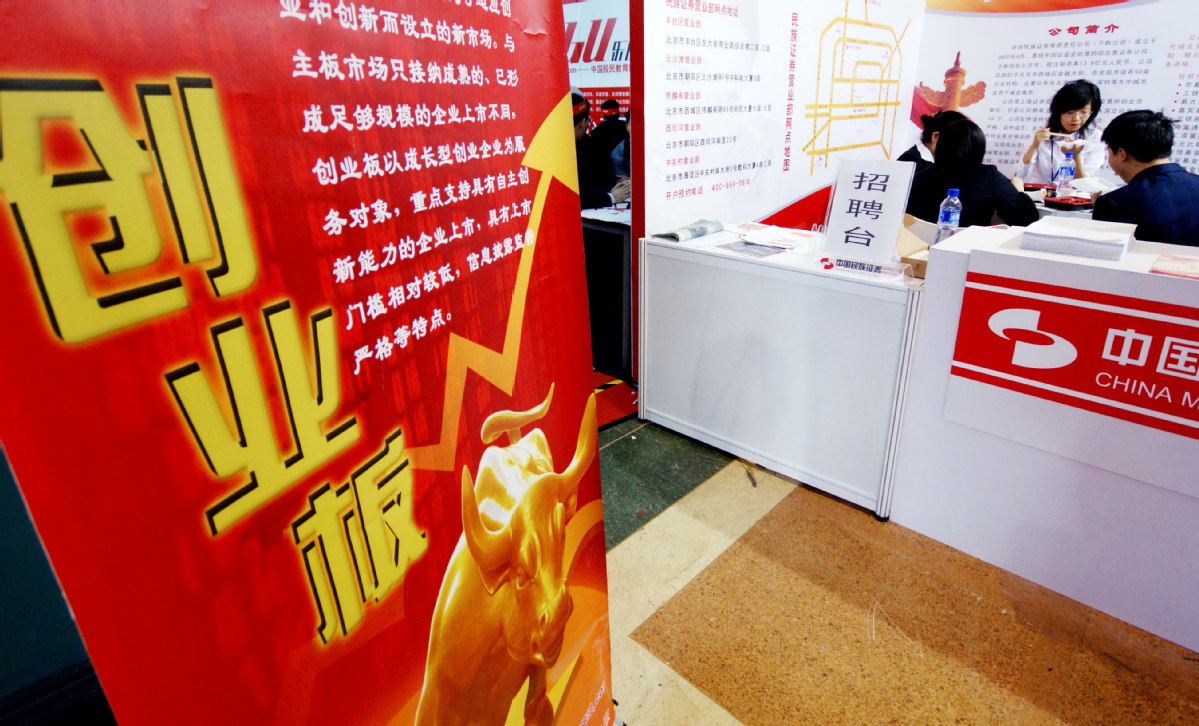
Eleven years after its creation, the startup board ChiNext on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange, which policymakers have hoped will become China's version of Nasdaq and a cradle of future Chinese technology giants, is embracing a big round of reform.
The reform is designed to change the fundamental rule of new share sales by introducing the registration-based initial public offering system on the board with an emphasis on information disclosure and market-based pricing.
On June 12, after soliciting public opinion on the draft rules, the country's securities regulator announced the official rules and regulations for the new IPO system. And from June 15, the Shenzhen Stock Exchange began accepting new IPO applications under the registration-based system.
Analysts and securities brokerages expect that the first batch of IPOs under the new listing system will be made in August.
Regulators, investors and industry experts have been hoping that the reform will bring about a fundamental transformation of the board by injecting new energy into the Shenzhen stock market, which has been competing with Shanghai and Hong Kong to attract promising and valuable innovative companies.
There have been concerns that ChiNext's role as the country's hub for incubating young and promising tech companies may be undermined by Shanghai, which first experimented with the registration-based IPO system on its technology-focused STAR Market last July.
But such concerns were soon dispelled after policymakers decided to replicate the successful practice in Shanghai in a wider marketplace.
ChiNext's new IPO system will underscore China's consistent pursuit of reform to boost the role of the capital market in serving the country's economic development.
A recent top-level meeting presided over by President Xi Jinping stressed the need to improve the fundamental system of the capital market. The larger goal is to build a "disciplined, transparent, open, vibrant, and resilient" equities market.
The timing of the reform is also crucial. It has been launched when the country is battling the impact of the COVID-19 epidemic. Many businesses, especially smaller firms, are struggling with financial difficulties and capital shortages.