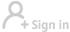The facts and China's position on China-US trade friction

5. The abuse of trade remedy measures
While the WTO allows the use of trade remedy measures when a member economy finds damage caused to its domestic industries by dumping, subsidy or excessive growth in imports, strict limits and conditions do apply. However, the US has resorted to a huge number of trade remedy measures to protect its domestic industries. Many of these measures target China.
The US is adopting a growing number of trade protectionist measures, whose share of the world's total is also rising. According to Global Trade Alert, among the 837 new protectionist measures adopted in 2017 worldwide, 143 (or 17.1 percent) were from the US. From January to the end of July in 2018, the US accounted for 33 percent of all protectionist measures in the world (Chart 10).
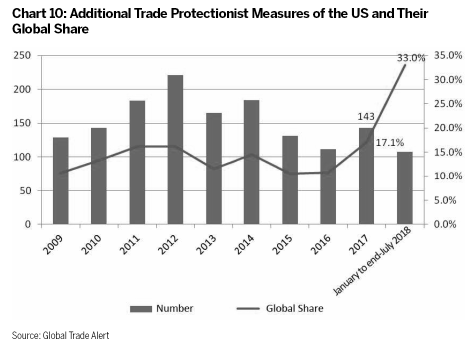
According to the United States International Trade Commission, by July 17, 2018 there were 44 anti-dumping and countervailing measures in effect in the US (Chart 11), among which 58 percent were adopted after the 2008 financial crisis, with China, the EU and Japan as the main targets.
In anti-dumping investigations, the US has refused to honor its obligation under Article 15 of China's WTO Accession Protocol and continued to use the surrogate-country approach, citing its domestic law. The Government Accountability Office (GAO) of the US Congress calculated that the rates of anti-dumping duties applied to countries recognized as market economies are notably lower than those applied to non-market economies (NMEs). The average anti-dumping duty imposed by the US on China is 98 percent, while that on market economies is 37 percent.51 Among the 18 US rulings concerning Chinese products since the start of 2018, 14 had rates of more than 100 percent. Moreover, the US picks surrogate countries rather randomly, 52 making the results of anti-dumping investigations highly unfair and discriminatory for Chinese exporters.